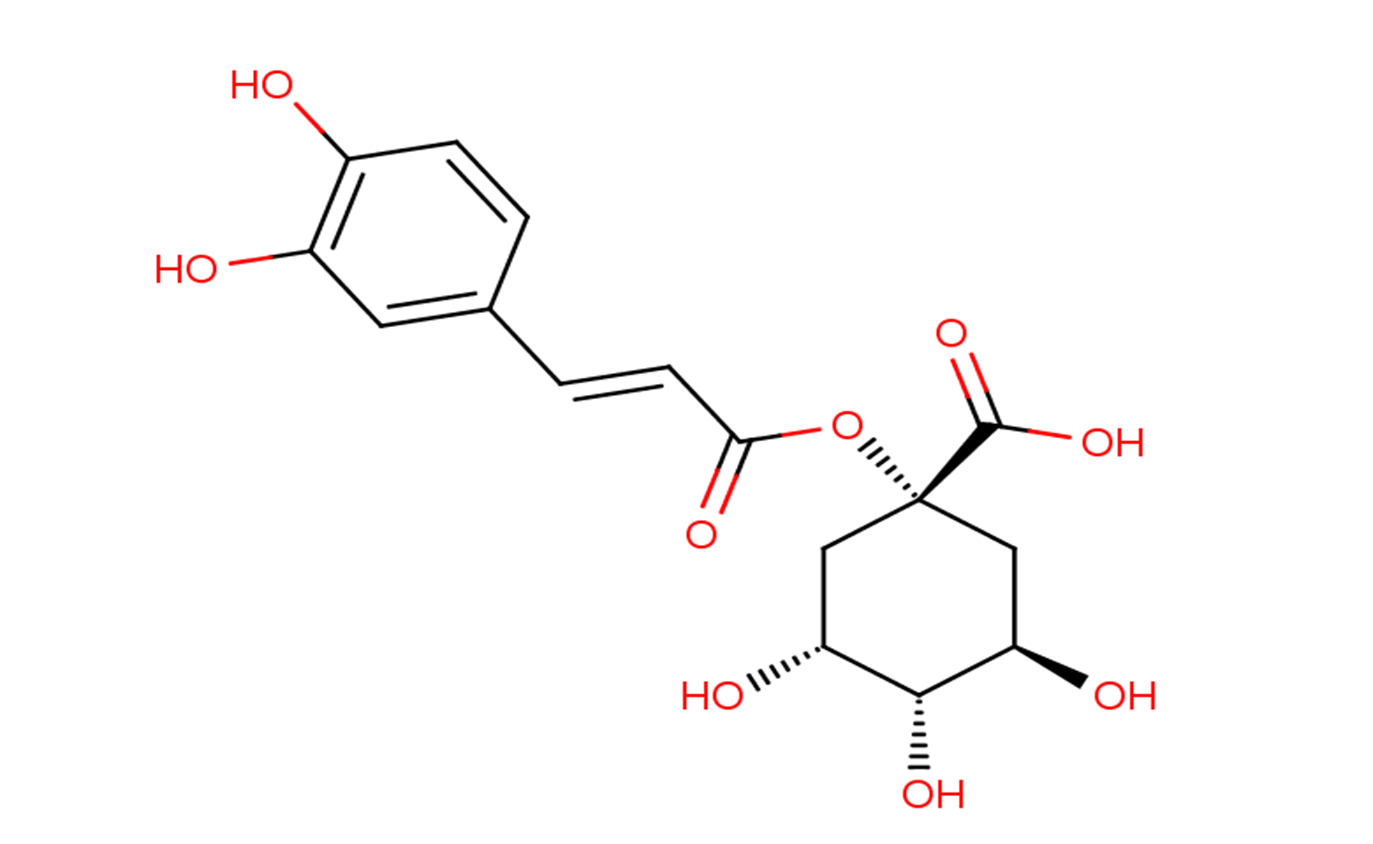
1-Caffeoylquinic acid
CAS No. 1241-87-8
1-Caffeoylquinic acid( —— )
Catalog No. M23415 CAS No. 1241-87-8
1-Caffeoylquinic acid is an important intermediate in lignin biosynthesis.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 383 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 556 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 866 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 1161 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 1575 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product Name1-Caffeoylquinic acid
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief Description1-Caffeoylquinic acid is an important intermediate in lignin biosynthesis.
-
Description1-Caffeoylquinic acid is an important intermediate in lignin biosynthesis. 1-Caffeoylquinic acid has anti-influenza, and antioxidant activities, it also slows the release of glucose into the bloodstream after a meal.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayApoptosis
-
TargetNF-κB
-
RecptorNF-κB
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number1241-87-8
-
Formula Weight354.31
-
Molecular FormulaC16H18O9
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO:10 mM
-
SMILESO[C@@H]1[C@H](O)C[C@@](OC(/C=C/C2=CC(O)=C(O)C=C2)=O)(C(O)=O)C[C@H]1O
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Qualitative and quantitative analysis of phenolics in Tetrastigma hemsleyanum and their antioxidant and antiproliferative activities.J Agric Food Chem. 2013 Nov 6;61(44):10507-15.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Polyphyllin I
Polyphyllin D induces apoptosis via the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway as evidenced by decreased Bcl-2 expression levels, disruption of MMP and increased Bax, cytochrome C, and cleaved-caspase-3 levels.
-
Anti-inflammatory ag...
Anti-inflammatory agent 51 is an amide/sulfonamide derivative with anti-inflammatory and potentially anti-tumor activity and inhibition of NF-κB activation, which can be used to study acute lung injury and ulcerative colitis.
-
Edasalonexent
Edasalonexent (CAT-1004) is a bifunctional, orally administered small molecule that covalently links 2 compounds known to inhibit NF‐κB, salicylic acid and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA).



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


